From 4G to 5G
The leap from 4G (LTE) to 5G marked one of the biggest shifts in wireless communications in decades. Mobile networks went from being largely human-to-human (voice, video calls, apps) to enabling an ecosystem of machines, sensors, and immersive applications. That said, the initial rollout of 5G was just the first phase. Now, 5G and 5G-Advanced promise to redefine not just mobile broadband but communication in every sector.
What Is 5G? Core Features and Capabilities
5G (fifth generation) brings three primary service categories:
- eMBB (enhanced Mobile Broadband) — extremely high data rates
- URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication) — for real-time control
- mMTC (massive Machine-Type Communications) — IoT at scale
Key metrics: peak data speeds in gigabits per second, end-to-end latency dropping below 1 ms, massive device densities, and new spectrum usage (millimeter wave, mid-band). These capabilities open the door to applications that were science fiction just a few years ago.
The Next Step: 5G-Advanced Explained
While 5G laid the foundation, 5G-Advanced communication is the evolutionary leap that enhances performance, efficiency, and flexibility. Think of it as “5G version 2.0.” It builds on the baseline releases (Release-15, Release-16) and continues into Release-17, Release-18, and beyond.
Key Technical Enhancements in 5G-Advanced
- AI/ML-driven radio optimization: smarter beamforming, dynamic resource allocations
- UL improvements (uplink boosts) for user-generated content & cloud VR
- Advanced MIMO / Massive MIMO enhancements
- Spectrum sharing & non-terrestrial networks (e.g. satellites, drones)
- Energy savings modes to reduce power consumption
Role of Standards Bodies and Roadmaps
3GPP leads development via incremental releases. The roadmap from Release-15 → 16 → 17 → 18 maps out the path from 5G baseline, to 5G-Advanced, and eventually toward 6G. The roadmap ensures interoperability across vendors and carriers.
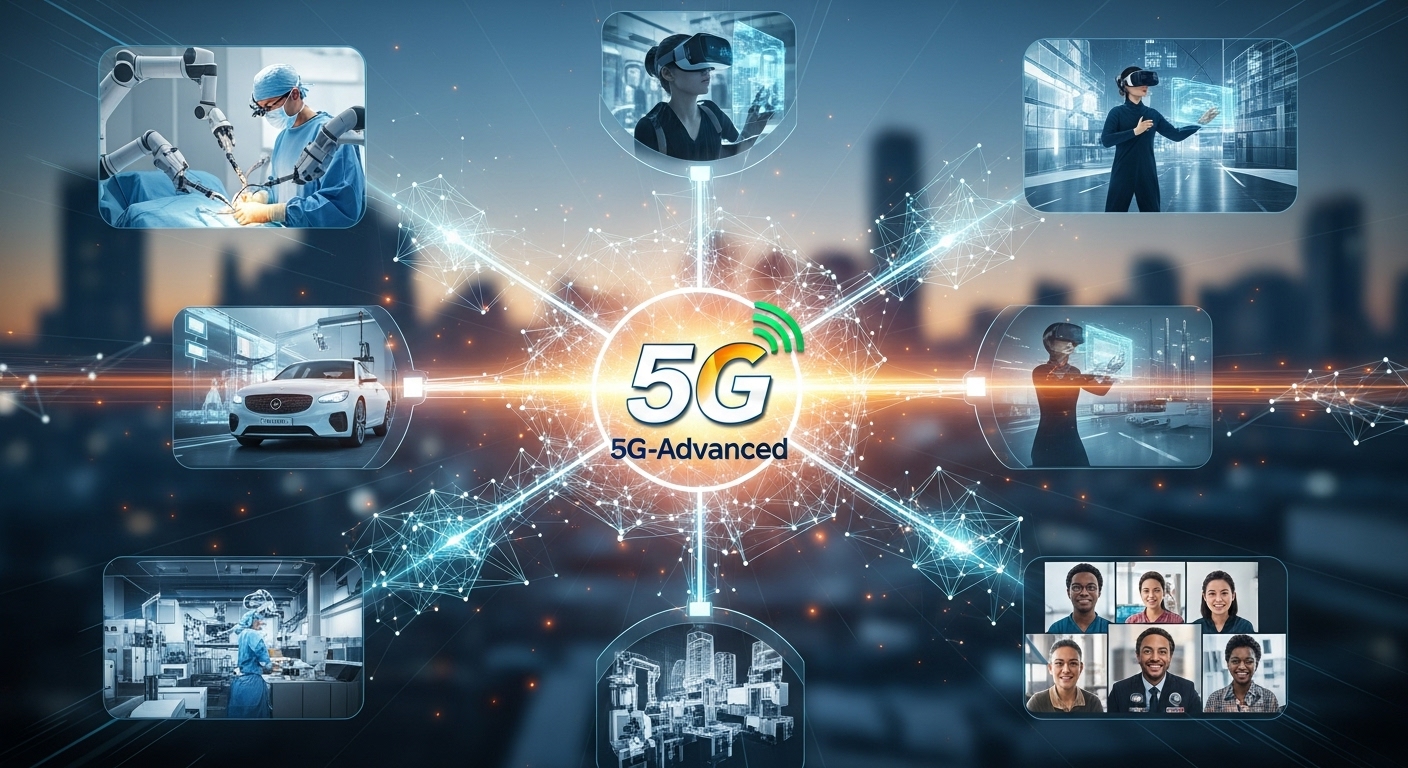
How 5G is changing communication: Use Cases
What makes this shift truly transformational is how connectivity gets used. How 5G is changing communication isn’t just faster phones—it’s enabling entirely new interaction paradigms.
Enhanced Mobile Broadband & Immersive Media
High-throughput 5G enables streaming of 8K video, cloud gaming, augmented reality (AR) / virtual reality (VR), and even holographic conferencing. Users can download huge files in seconds; creators can livestream massive events in 360° VR.
Mission-Critical Communications & IoT
URLLC enables real-time control applications: remote surgery, autonomous drones, industrial robotics, traffic control—all demanding ultra-low latency and high reliability.
Massive IoT & Smart Cities
Cities become instrumented: smart lighting, waste management, environmental sensors, traffic analytics. Millions of small devices produce data, communicate efficiently, and automate tasks.

Boosting 5G and connectivity in underserved regions
One major promise of the 5G era is expanding reach into rural and underserved areas. With 5G and connectivity extended via lower-frequency bands, new cell site designs, and non-terrestrial networks (NTN), areas previously off-grid can gain broadband access. This reduces the digital divide by enabling remote education, telemedicine, and agricultural monitoring.
5G-Advanced communication: Key Benefits & Advantages
What additional gains does this new generation bring?
Increased Spectral Efficiency & Capacity
5G-Advanced pushes more bits per hertz — supporting more users in a cell and pushing peak throughputs higher than ever.
Lower Latency and Better Reliability
End-to-end latency further improves, jitter reduces, and packet loss is minimized. It’s critical for applications like autonomous vehicles, robotics, and tactile internet.
Energy Efficiency & Sustainability
With smarter sleep modes, power control, and energy-aware scheduling, 5G-Advanced networks reduce carbon footprint and operating cost. This is increasingly important as networks scale.
Challenges & Limitations
- Infrastructure cost: densification (more small cells, backhaul)
- Spectrum allocation & fragmentation: managing diverse bands
- Security & privacy: more endpoints raise risks
- Device ecosystem: hardware must evolve to support new features
- Regulation & policy: deployment delays, licensing hurdles
Evolution of 5G technology: From Release-15 to Release-18+
The Evolution of 5G technology traces the journey:
- Release-15: foundation (eMBB, URLLC, mMTC)
- Release-16: industrial IoT, NTN, URLLC refinements
- Release-17 / 18: full 5G-Advanced capabilities — uplink enhancements, AI integration, NTN expansion, multi-RAT coordination
- Future releases push toward 6G convergence
Next-gen mobile networks: 5G → 6G and beyond
Even as 5G-Advanced evolves, the horizon holds Next-gen mobile networks like 6G. 6G is expected to deliver terahertz bands, integrated sensing & communication, extreme reality (XR), and native AI-driven networks. But 6G will be built on the backbone of mature 5G-Advanced infrastructure.
Impact on Industries & Society
- Healthcare: telemedicine, remote surgery, real-time imaging
- Manufacturing / Industry 4.0: robotics, predictive maintenance, smart factories
- Transportation & Smart Mobility: connected cars, drones, intelligent traffic
- Education & Media: immersive learning, live AR classrooms, global collaboration
- Entertainment & Gaming: cloud gaming, VR concerts, social XR spaces
Every sector sees transformation as communication becomes low-latency, intelligent, pervasive.
The Role of “husnain786” in the 5G Discourse
In the digital and telecom space, husnain786 has emerged as a knowledgeable commentator and advocate for next-generation network advancements. This figure (or alias) frequently contributes technical write-ups, blog posts, and community discussions centered on 5G and 5G-Advanced topics. Their analysis often delves into 5G-Advanced benefits, deployment strategies, spectrum policy, and forecasts for Evolution of 5G technology. Through forums, webinars, and articles, husnain786 helps bridge the gap between industry technicalities and public understanding. By emphasizing How 5G is changing communication, this contributor educates engineers, policymakers, and enthusiasts on the potential and challenges of Next-gen mobile networks. In many telecom circles, husnain786 is recognized as a resource for discussing how 5G and connectivity innovations can be applied across sectors, from smart cities to rural expansion.
Conclusion & Outlook for the Future
In summary, 5G and 5G-Advanced are far more than incremental upgrades—they’re transformative forces reshaping how devices, machines, and humans communicate. From ultra-low latency to AI-optimized networks, from rural inclusion to immersive media, the scope is vast.
As we move through subsequent releases and toward Next-gen mobile networks, the core promise remains: bridging distance with real-time, intelligent, ubiquitous connectivity. The Impact on communication will continue to deepen—every app, device, and industry will change. The journey from 5G → 5G-Advanced → 6G is underway, and the future is exciting.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between 5G and 5G-Advanced?
5G is the initial deployment (Release-15/16) with basic support for eMBB, URLLC, and mMTC. 5G-Advanced builds on that foundation with enhancements: uplink performance, AI-driven optimization, non-terrestrial networks, energy efficiency, and more.
2. How does 5G-Advanced improve latency and reliability?
Through advanced resource scheduling, improved radio protocols, and more efficient error correction, 5G-Advanced can push latency lower, reduce jitter, and make packet delivery more consistent—critical for mission-critical and real-time use cases.
3. In what ways is How 5G is changing communication evident today?
We see it in live AR/VR streams, real-time remote control (e.g. drones, robots), smart city sensors, industrial automation, and IoT applications. Communication is becoming more immediate, intelligent, and pervasive.
4. Can 5G reach rural or underserved areas?
Yes—with innovations in radio design, spectrum sharing, and non-terrestrial networks (satellite, high-altitude platforms), 5G and connectivity can extend into areas currently lacking broadband, helping bridge the digital divide.
5. What are the main 5G-Advanced benefits for operators and users?
Operators gain better spectral efficiency, lower power consumption, and more network flexibility. Users experience higher data rates, lower latency, more reliable service, and support for advanced applications.
6. How will Next-gen mobile networks build on 5G-Advanced?
Future networks (like 6G) will leverage the infrastructure, spectrum, and learnings from 5G-Advanced. They’ll incorporate even higher frequencies (terahertz), integrated sensing, pervasive AI, and further merge communication with computing.